| Type |
Werk.Nr |
Registration |
History |
| Be 51-139 |
|
BV+AD |
|
| Be 51-139 |
|
BV+AK |
|
| Be 51-139 |
|
BV+AZ (BZ+AZ ?) |
|
| Be 51-139 |
|
BZ+AL |
FFS A/B 23 |
| Be 51-139 |
|
BZ+AQ |
|
| Be 51-139 |
|
BZ+AV |
|
| Be 51-139 |
|
FK+IJ |
|
| Be 51-139 |
|
GA+AB |
FFS A/B 71 |
| Be 51-139 |
|
NH+ML |
|
| Be 51-139 |
|
PK+IH |
FFS A/B 119 |
| Be 51-139 |
|
??+AY |
FFS A/B 4 |
| Be 51-139 |
|
??+KY |
FFS A/B 4 |
| Units |
| FFS (A) 71, |
Prossnitz |
| FFS (A/B) 14 |
Klagenfurt |
| FFS (A/B) 23 |
Kaufbeuren |
| FFS(A/B) 62 |
Vöslau |
| Sch/Fl. Ausb. Rgt. 62 |
Trausdorf |
| FFS(A/B) 71 |
Prossnitz |
| FFS(A/B) 114 |
Weimar-Nohra |
| FFS(A/B) 119 |
Jüterbog-Damm |
| FFS A/B 4 |
Neudorf/Oppeln |
| Type |
2 -seat trainer |
| Engine |
1 Walter Minor 4-I |
| Dimensions |
Length 7,85 m, height 2,05 m , span 11,42 m , wing area 15,25 m2 , |
| Weights |
Empty 480 kg, loaded , max. take off weight 760 kg |
| Performance |
Max.. speed 205 km/h , cruising speed 180 km/h , ferry range 1600 km, practical range 780 km, endurance , service ceiling 5000 m , climb |
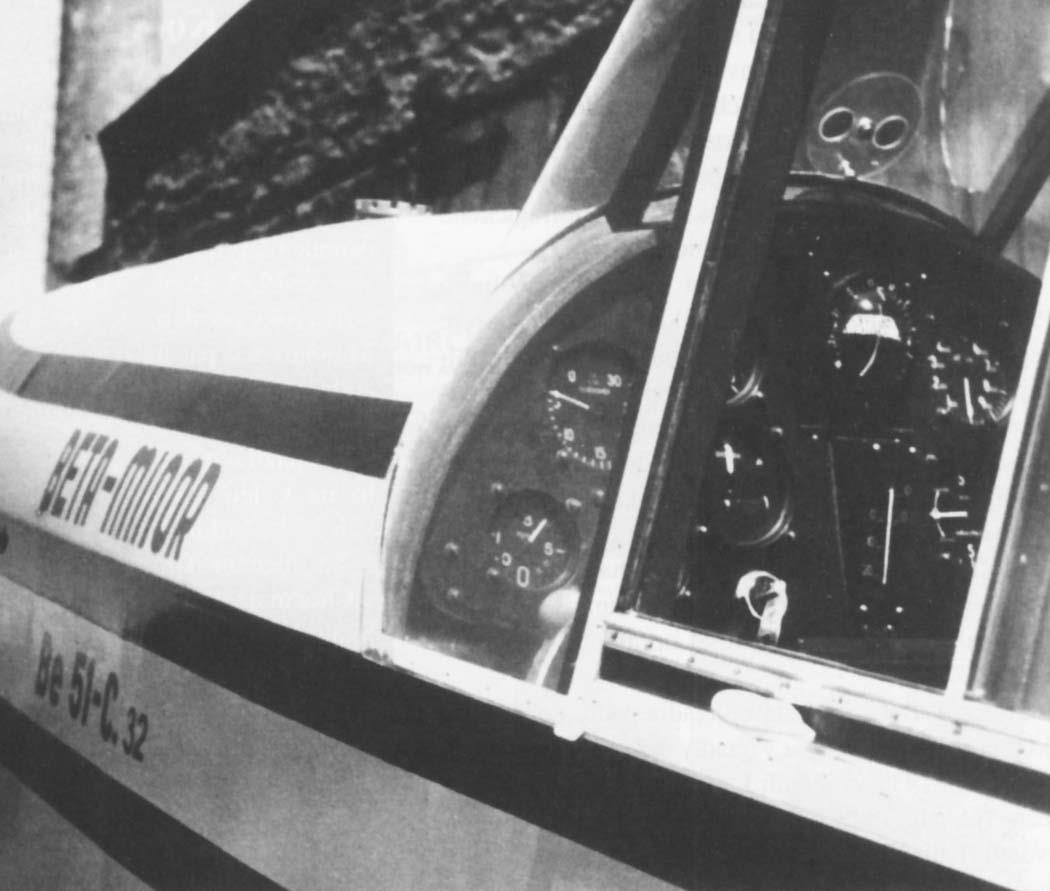

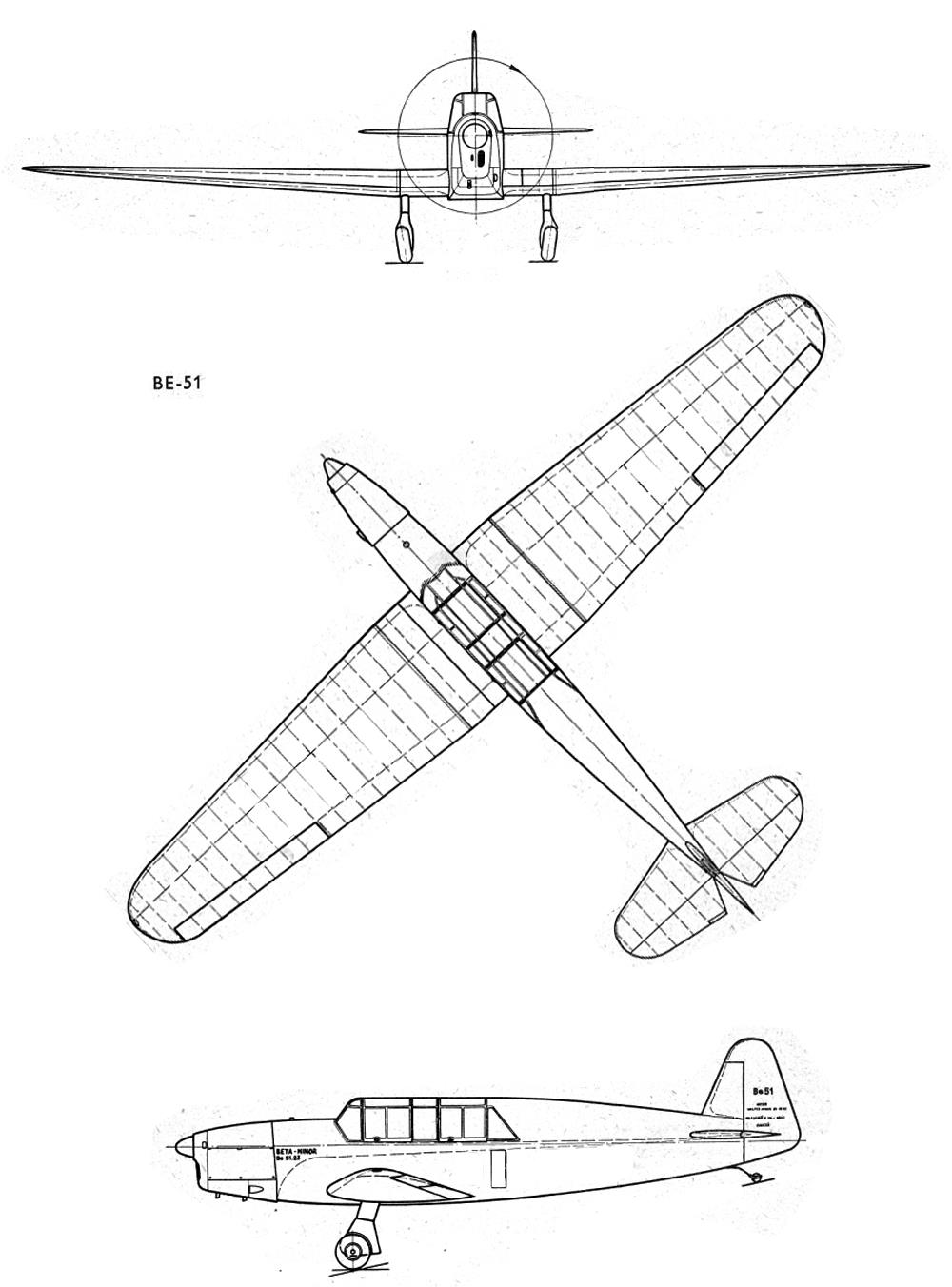


To consolidate the success of the Be.50, Benes-Mraz developed an upgraded version of the aircraft, the Be.51 . The main difference of the new aircraft was the closed cockpit. In addition, the Be.51 Beta Minor had a slightly reduced wing span.
The Be.51 light sports aircraft was built shortly before the start of the war (in October 1936, the first prototype flew into the air, and mass production began the following year) and was placed at the disposal of private aviation clubs. A total of 65 copies of the machine were produced.
In 1939, most of these aircraft were located on the territory of Slovakia and were included in its Air Force. A total of 25 planes were used.
The machine turned out to be successful, and after the annexation of Czechoslovakia, the German Luftwaffe used a large number of these aircraft for communication and training.











