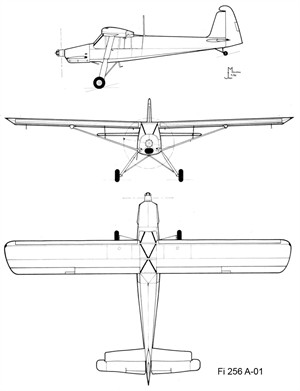
| Type | 1 + 3/4 passengers, Liason aircraft |
| Engine | 1 Argus As 10P |
| Dimensions | Length 9,62 m , height , span 14,50 m , wing area 24 m2 , aspect ratio 8,8 |
| Weights | Empty 1140 kg, loaded , max. take off weight 1750 kg |
| Performance | Max.. speed 215 km/h, cruising speed 200 km/h, range 700 km (with extra tank 1000 km), stall speed 59 km/h, landing speed 72 km/h, endurance , service ceiling 4200 m , climb to 4000 min. 20,9 min., take off 87 m - 45 m with 5 m/sec. head wind |


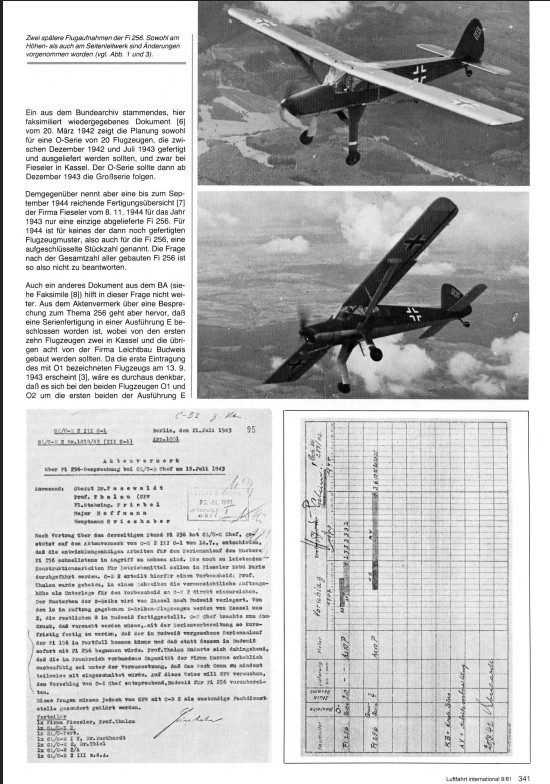

The aircraft was developed on the basis of the Fieseler Fi 156. The aircraft was similar in structure to the Fi 156, but had been structurally simplified and slightly enlarged so that five people (one pilot in the front and four passengers in the back) could be accommodated. The presentation of the design to the Reich Ministry of Aviation on 25 September 1940 was successful and series production was planned from spring 1941. The maiden flight of the Fi 256 V1 with Willy A. Fiedler at the controls took place on 9 July 1941 in Kassel-Waldau, whereby problems with the rudder arose during further testing, which made modification necessary. In addition, the shape of the elevators was changed to trapezoidal and moved slightly downwards. The second prototype, the V2, had its maiden flight in the fall of 1941, the V3 to V6 followed from the spring of 1942. In addition to the at least nine test samples produced, five more of twenty machines planned as pre-series examples were probably produced in Erfurt between December 1942 and the end of 1943 by the Otto Schwade company. The actual series production never took place, as other aircraft types were given a higher priority.
The machines manufactured were used as personal transport machines (for example by Gerhard Fieseler). Today, no specimen exists.
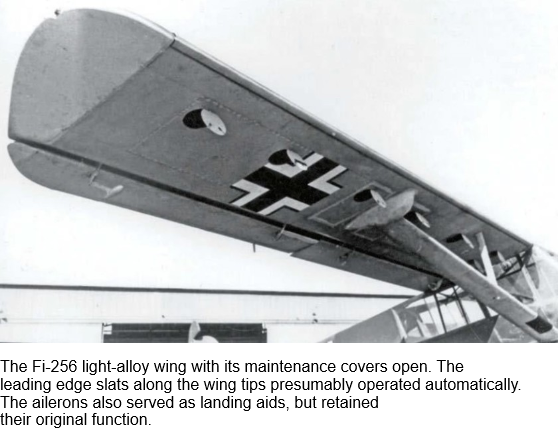
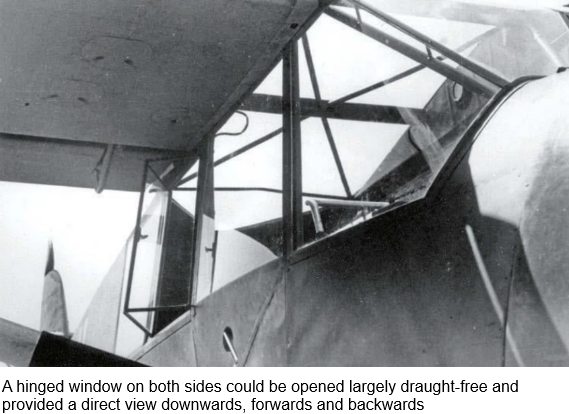
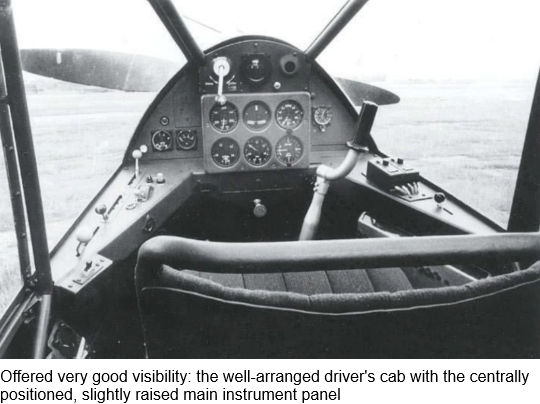
The focus of the development was on doubling the range to 700 km and increasing the maximum flight speed from 175 to 215 km/h, while retaining the remaining parameters (such as good slow flight characteristics and the engine). Above all, the aerodynamics have been improved. The cabin windows were installed flush with the fuselage instead of protruding and the wings were equipped with automatically extending slats. The modified low-drag landing gear, which was attached directly to the fuselage in a cantilevered manner, was tested on a Fi 156 (registration D-IGQE). Hardly any wood was used for the structure. For example, the planking of the two-spar wings and a large part of the tubular steel fuselage framework consisted of aluminum sheets. Only for rudders and flaps a fabric covering was used.
The machines manufactured were used as personal transport machines (for example by Gerhard Fieseler). Today, no specimen exists.
The focus of the development was on doubling the range to 700 km and increasing the maximum flight speed from 175 to 215 km/h, while retaining the remaining parameters (such as good slow flight characteristics and the engine). Above all, the aerodynamics have been improved. The cabin windows were installed flush with the fuselage instead of protruding and the wings were equipped with automatically extending slats. The modified low-drag landing gear, which was attached directly to the fuselage in a cantilevered manner, was tested on a Fi 156 (registration D-IGQE). Hardly any wood was used for the structure. For example, the planking of the two-spar wings and a large part of the tubular steel fuselage framework consisted of aluminum sheets. Only for rudders and flaps a fabric covering was used.