| Type |
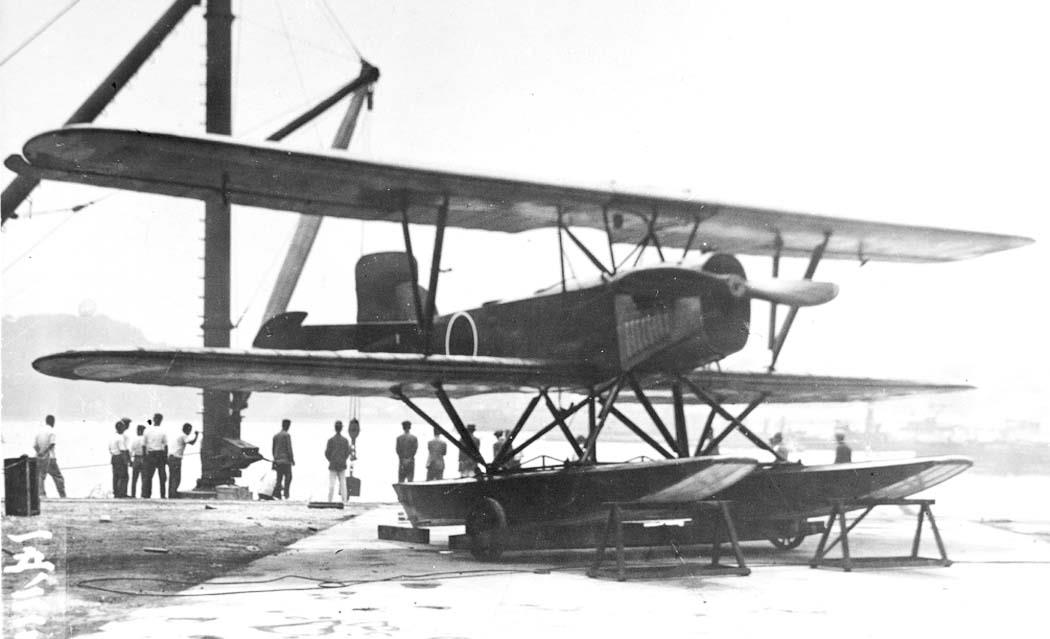
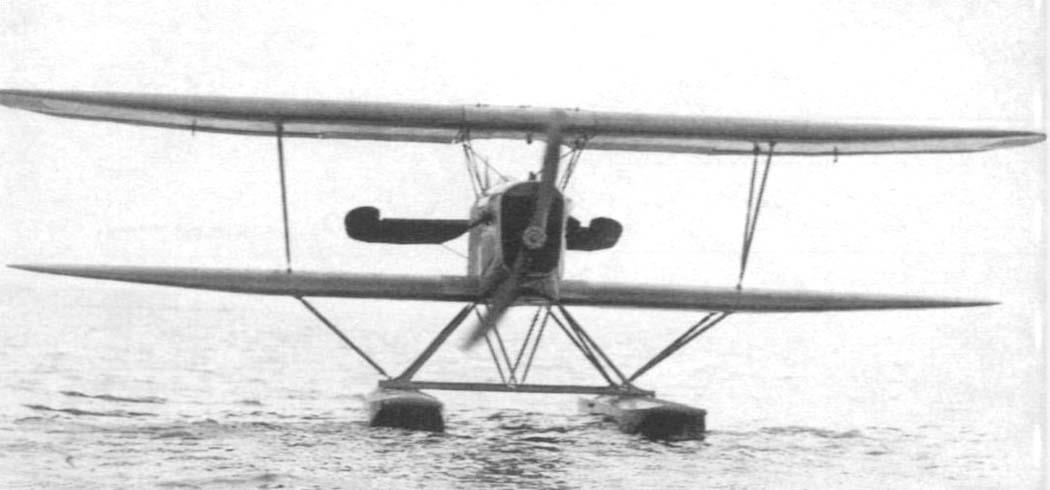
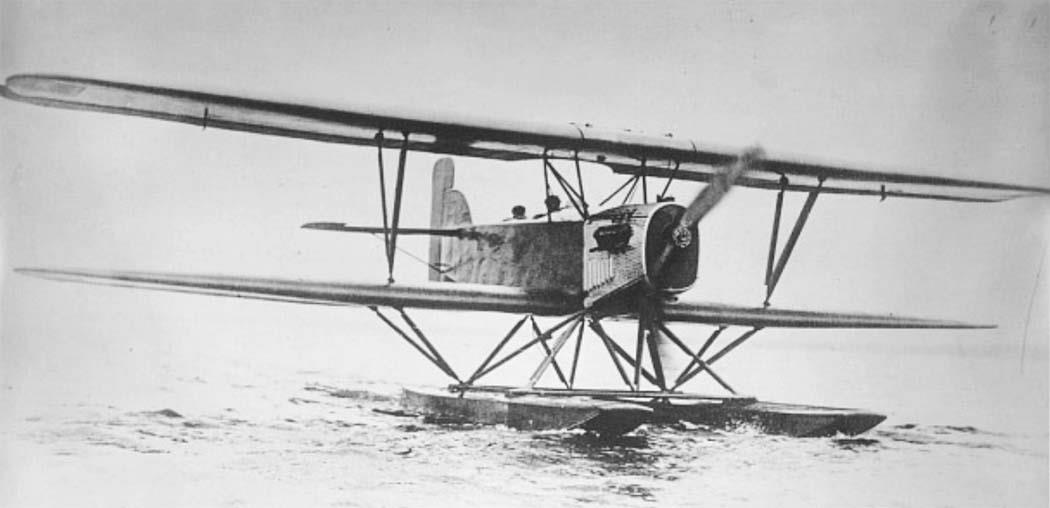
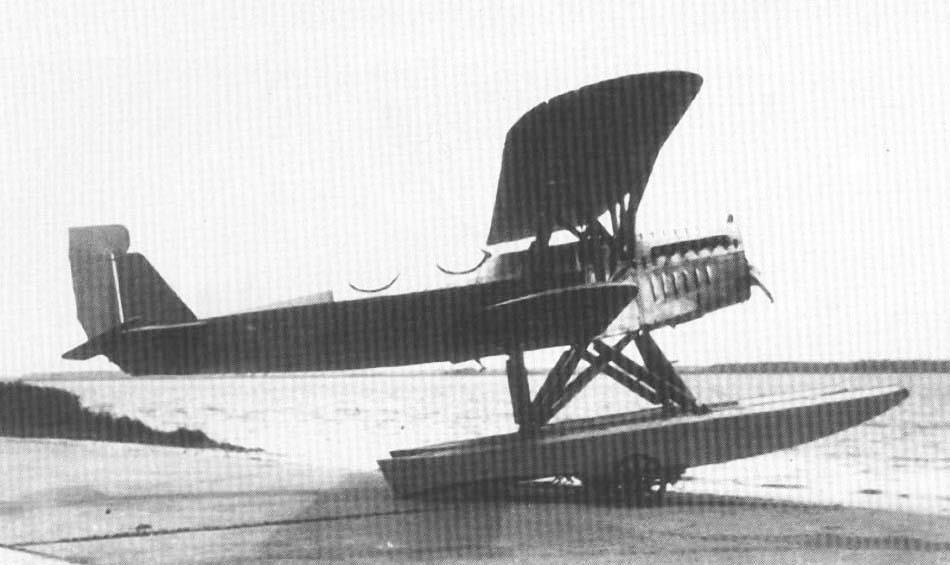
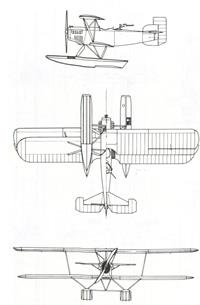
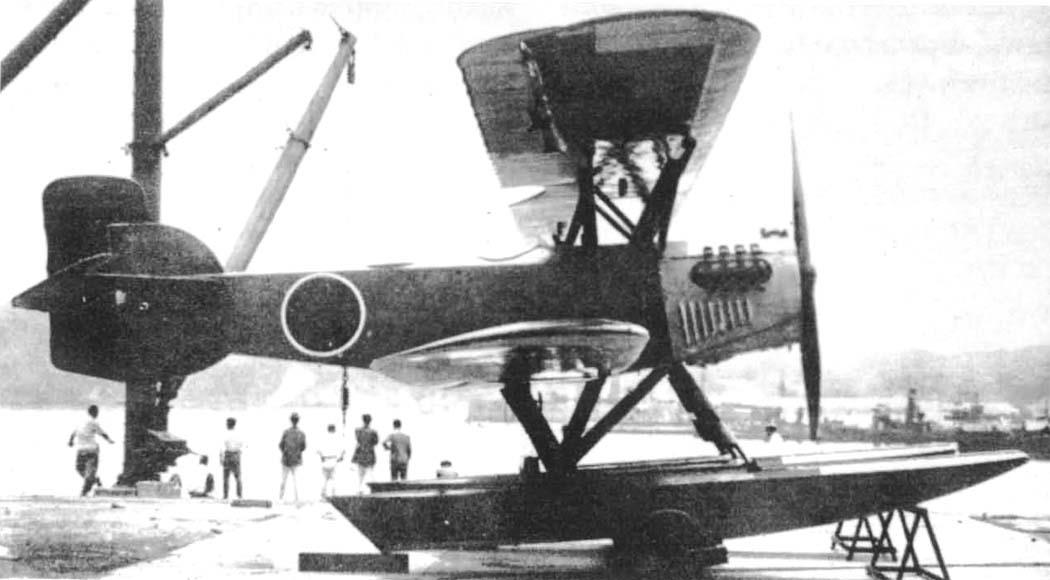
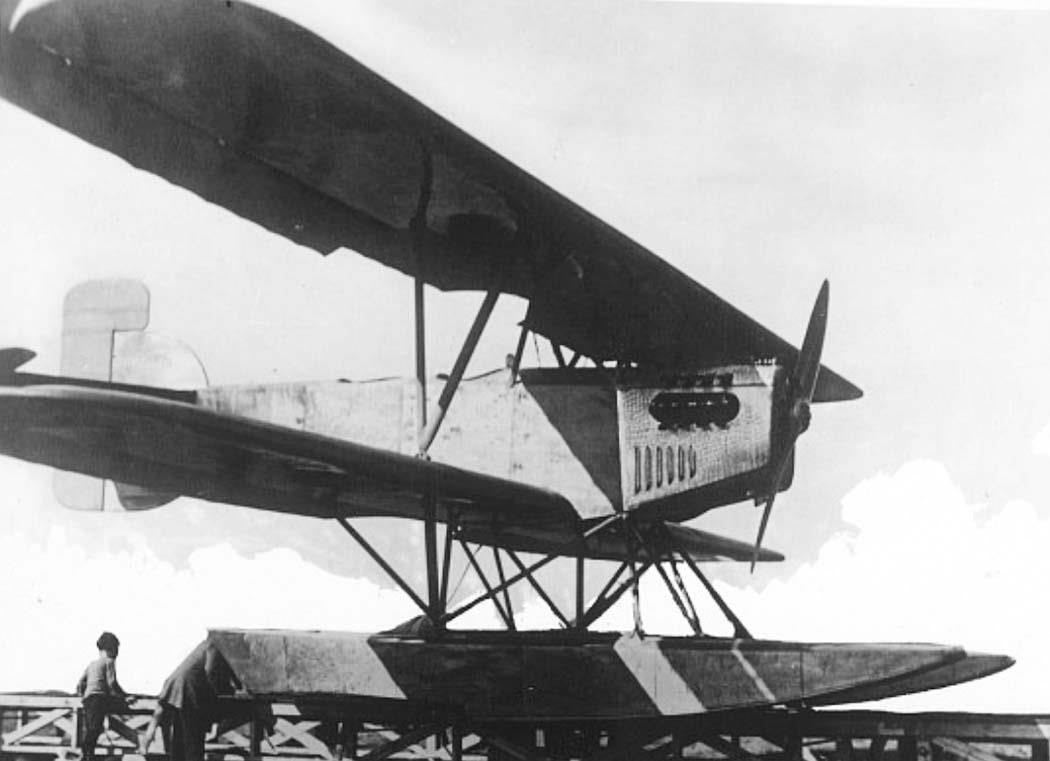
2-seat reconnaissance floatplane (Aichi Type 2) |
| Engine |
1 Napier Lion |
| Dimensions |
Length 9,60 m, height 4,27 m, wingspan upper 14,85 m, lower 14,15 m, wing area 55,8 m2 |
| Weights |
Empty 1550 kg, flying weight 2500 kg, fuel 900 l in a tank above fuselage in mid section of wing |
| Performance |
Max. speed 190 km/h, range 920 km, climb to 1000 m 3,0 min., to 2000 m 6,2 min., endurance 4,5 h, service ceiling (full load) 5800 m, landing speed 77 km/h |
| Armament |
1 flexible rearward-firing 7,7 mm machine gun , 4 30 kg bombs |