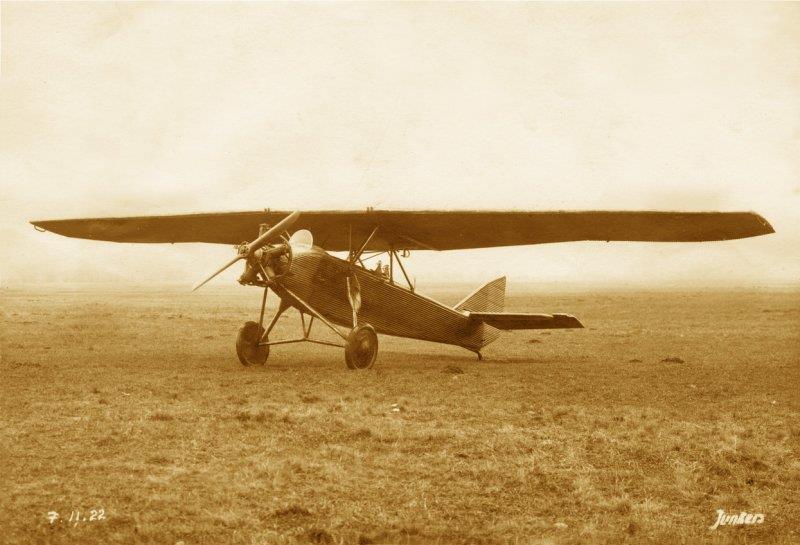
| Type |
1 + 2 seat trainer and sportplane |
| Engine |
1 Junkers L1 |
1 Armstrong Siddeley Genet |
1 Siemens Sh 5 |
1 Siemens Sh 12 |
1 Siemens Sh 4 |
| Dimensions |
Length , height , span , wing area , |
Length 6,12 m, height 2,77 m, span 11,25 m, wing area 19,0 m2 |
Length 6,85 m, height 2,75 m, span 11,25 m, wing area 19,00 m2 |
Length 6,85 m, height , span 11,25 m, wing area 19,0 m2 |
Length 6,85 m, span 11,25 m, wing area 19,0 m2 |
| Weights |
Empty , loaded , max. take off weight |
Empty 525 kg, flying weight 761 kg |
Empty 525 kg, flying weight 765 kg |
Empty 545 kg, flying weight 780 kg |
Empty 545 kg, flying weight 780 kg |
| Performance |
Max.. speed , cruising speed , range , endurance , service ceiling , climb |
Max. speed 134 km/h, cruising speed 109 km/h, service ceiling 3962 m |
Max. speed 133 km/h, cruising speed 105 km/h, range 360 km, |
Max. speed 160 km/h, range 420 km |
|