B
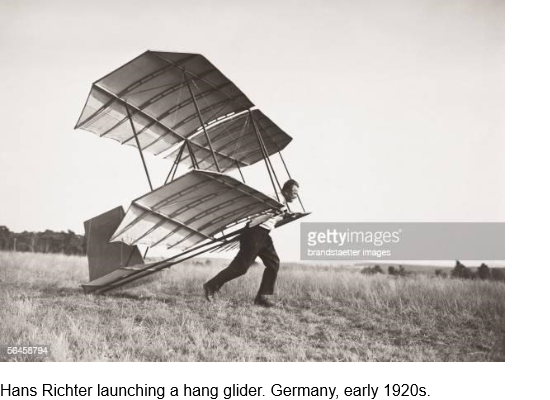
Richter unternahm 1908 als Gymnasiast in Swinemünde erste Gleitflugversuche. Ab 1910 konstruierte er verschiedene Gleitflugzeuge (Hängegleiter), mit denen er Schauflüge u. a. auf den Flugplätzen in Johannisthal und Stölln bei Rhinow ausführte. Dort teste er unter anderem einen von ihm erworbenen, von Waldemar Geest entwickelten Gleitflieger, die „Weih“. Ab 1912 wurde Richter zum Flugzeugführer ausgebildet und diente im Ersten Weltkrieg bei verschiedenen Feldfliegerabteilungen. Nach seiner Dienstuntauglichkeit ließ er sich von Friedrich Wilhelm Conrad Horster zum Zauberkünstler ausbilden und nahm den Künstlernamen Ernin an.
Ab 1923 baute er sechs Rekonstruktionen der Flugapparate Otto Lilienthals für Museen in Anklam, Berlin, München, Meudon u. a. 1924 drehte Richter mit ihm selbst als Lilienthal-Darsteller und seiner Rekonstruktion von dessen Flugapparat einen Stummfilm mit dem Titel Otto Lilienthal, der Altmeister der Fliegekunst[
First hydroplaneur with pneumatic floats
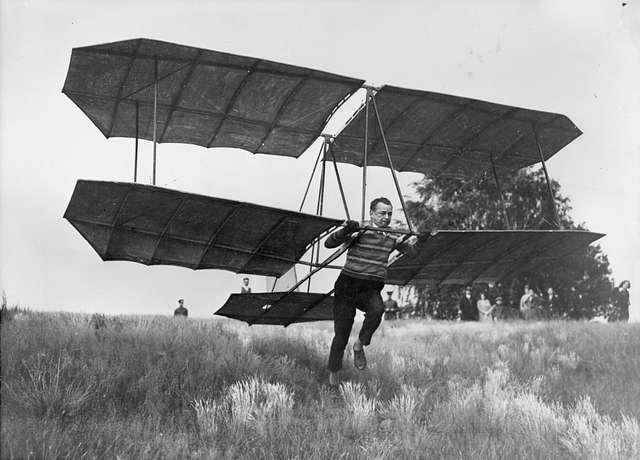
History summaryThe success of the Rhön glider pilots have demonstrated that it is possible to navigate in favorable wind conditions in mountainous terrain for hours in the rising wind. The maximum performance sailing continuous flight of the mountain presented at the East Prussian teacher Ferdinand Schulz. All these flights were made, but dunes or hills, where a strong wind, stable or increasing navigate very favored. The next and most important step in motorless flight departs flat terrain. The first experiments of this kind have been made by former glider after Otto Lilienthal, the master of aerobatics, Hans Richter, who has been dealing since 1907 with the gliding. He flew on January 9, 1913, a glider of 14 square meters on the Tempelhof field in Berlin from ground level and topped with routes 10 to 12 meters in length about 2 to 4 meters high. The start was made with the launch of simple foot (start) to about 6 meters wind. Other experiments they conducted a few months in 1913 on Johannisthaler airfield, where he was a shed made available by Major by Tschudy. The reason for the success was moderate while the low starting strength. Only in October 1926 under the judge took new tests in a glider Tempelhof Airport in Berlin, where he had put his glider of a motorcycle. Here, a flight was made in about 20 meters high and 300 meters long.
Two pneumatic WasserschmimmerSchon long been looking for an easy float to allow a departure from the judge of the water. He exhibited there is such a float rubberized cloth, which is filled with air, are hardly surpassed in ease, but they weigh only 2 kg. Our first illustration shows these swimmers.
For airplanes these swimmers will also be a significant improvement, particularly in terms of weight. There are, however, several partitions installed and stiffeners if necessary, so that the title is given to a shock that way for fixed planes.
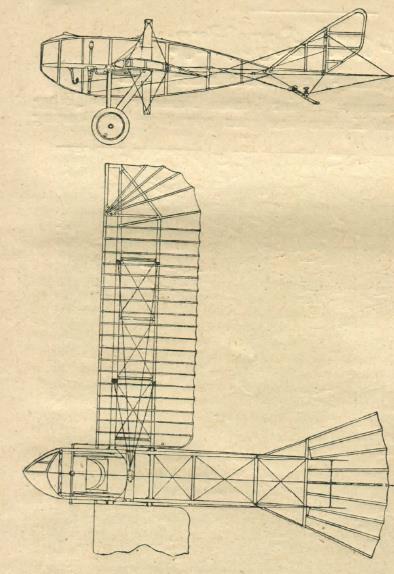
The reproduced in our second water glider illustration is only 6 meters wide, has 18 square feet of wing and weighs 1.5 quintals. It is easy to disassemble, and surfaces in three parts, each 2 meters long, so it can be housed in small spaces without any difficulty. The floats are broken and can be kept in a large towel.
Hans Richter Der starting water is done using a boat powerful engine that pulls the airplane in the wind, which is slightly raised above the water. By pneumatic float a particularly smooth landing is assured. Thus, a new sport will grow from this opportunity should not be overlooked. The aircraft represented a cost of about 400 marks, so it is affordable for any sports man soon.