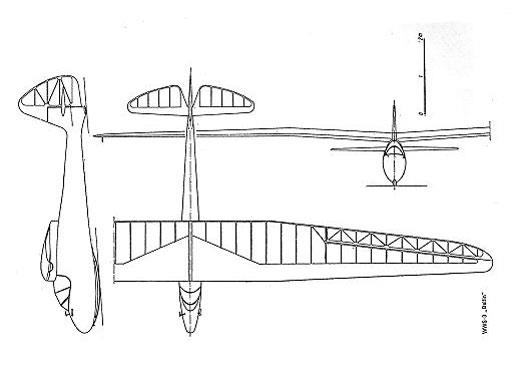
| Type | Single seat glider |
| Dimensions | Length 6,97 m, height 1,7 m, span 16 m , wing area 20,15 m2 , aspect ratio 12,7 |
| Weights | Empty 135 kg, loaded 232 kg |
| Performance | Max.. speed 200 km/h, stall speed 39 km/h, max. glide ratio 21,4 at 52 km/h, rate of sink 0,61 m/sec., G limits 5,5/ - ? g |
| Type | Werk.Nr | Registration | History |
| 1297 | |||